恶性胸腔积液(MPE)是晚期肺癌、乳腺癌等常见并发症,因胸膜转移、血管渗透性增加及淋巴引流受阻等多因素导致,治疗上存在复发率高、疗效短暂、副作用强等难题1-4。传统治疗如胸腔穿刺、硬化剂固定术、胸腔注药和免疫靶向疗法均存在局限性,难以实现长期控制2,5-7。胸膜腔独特的生理环境——如持续变化的负压(-3至-10 mmHg)与富氧状态,既是挑战,也为新型治疗策略提供契机8。
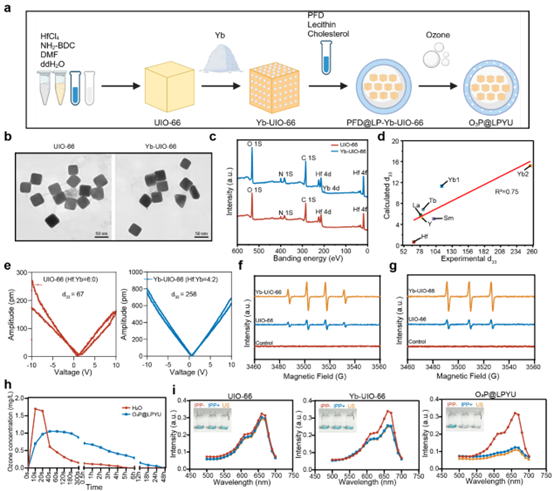
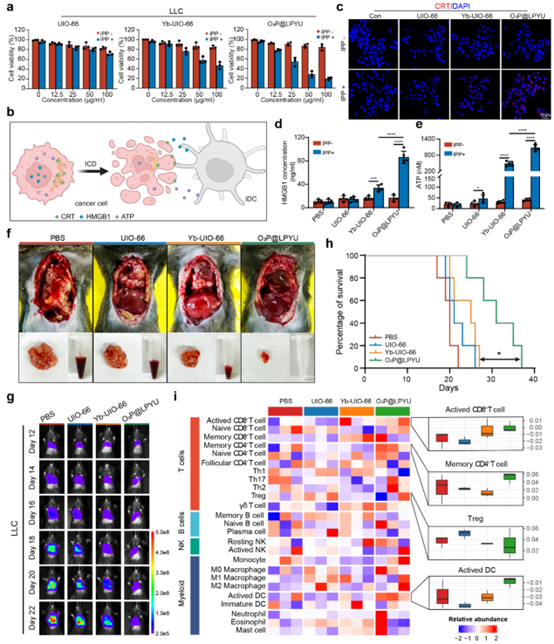
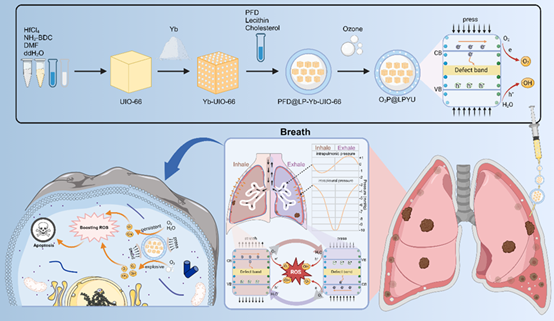
四川大学华西医院乳腺健康医学研究院石虎兵团队于2025年4月在Nature Communications发表研究论文Intrapleural Pressure-controlled Piezo-catalytic Nanozyme for the Inhibition of Malignant Pleural Effusion。本研究基于胸膜腔独特的生理环境特点,构建了一种基于生理性胸膜腔压力变化响应的压电纳米系统O₃P@LPYU,利用稀土掺杂增强MOF材料的压电性能,使其在呼吸过程中无需外部刺激即可自发激活催化反应,持续产生活性氧,有效诱导肿瘤细胞发生免疫原性死亡,显著抑制恶性胸腔积液进展。

文章结论与讨论,启发与展望
本研究首次将生理性压力变化与压电催化结合,实现了MPE的“自驱动”治疗模式。通过Yb掺杂优化材料性能,结合臭氧缓释,实现了高效、低毒的肿瘤微环境调控。未来有望通过临床转化,为晚期癌症患者提供更优解。
本文第一单位为四川大学华西医院,乳腺健康医学研究院敬静教授、石虎兵教授及浙江大学医学院卓巍教授为共同通讯作者;乳腺健康医学研究院许子寒博士后、何秀静助理研究员、贵昱博士和成都大学药学院唐凌凯硕士为共同第一作者。
原文链接 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-58354-9
参考文献:
- Maskell NA. Treatment options for malignant pleural effusions: patient preference does matter. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association, 2012, 307:2432-2433.
- Gayen S. Malignant pleural effusion: Presentation, diagnosis, and management. American Journal of Medicine, 2022, 135:1188-1192.
- Gonnelli F, Hassan W, Bonifazi M, et al. Malignant pleural effusion: current understanding and therapeutic approach. Respiratory Research, 2024, 25:47.
- Egan AM, McPhillips D, Sarkar S, et al. Malignant pleural effusion. Qjm-an International Journal of Medicine, 2014, 107:179-184.
- Thomas R, Fysh E, Smith NA, et al. Effect of an indwelling pleural catheter vs talc pleurodesis on hospitalization days in patients with malignant pleural effusion: The AMPLE randomized clinical trial. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association, 2017, 318:1903-1912.
- Figlin R, Mendoza E, Piantadosi S, et al. Intrapleural chemotherapy without pleurodesis for malignant pleural effusions. LCSG Trial 861. Chest, 1994, 106:363S-366S.
- Donnenberg AD, Luketich JD, Dhupar R, et al. Treatment of malignant pleural effusions: the case for localized immunotherapy. Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer, 2019, 7:110.
- DeBiasi EM, Feller-Kopman D. Physiologic basis of symptoms in pleural disease. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2019, 40:305-313.
供稿:许子寒
编辑:贵昱